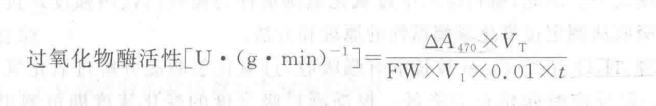Determination of catalase (POD) activity
To understand the principles and methods of colorimetric determination of peroxidase activity.
Principle
Peroxidase (POD) catalyzes the reaction of oxidation of phenolics by hydrogen peroxide, the product being a Da-like compound, this compound is further condensed or condensed with other molecules to produce a darker colored compound. In this experiment, o-methoxyphenol (i.e., guaiacol) was used as the substrate of peroxidase, and in the presence of this enzyme, H2O2 oxidized o-methoxyphenol to reddish-brown 4-o-methoxyphenol, which can be used to determine its absorbance value by a spectrophotometer at 470 nm, which can be used to find out the activity of the enzyme. The reaction is: 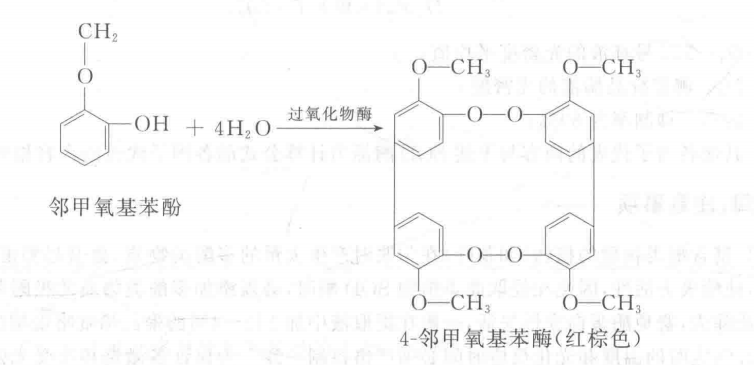
Operation method
Determination of catalase (POD) activity
Principle
Peroxidase (POD) catalyzes the reaction of oxidation of phenolics by hydrogen peroxide, the product being a Da-like compound, this compound is further condensed or condensed with other molecules to produce a darker colored compound. In this experiment, o-methoxyphenol (i.e., guaiacol) was used as the substrate of peroxidase, and in the presence of this enzyme, H2O2 oxidized o-methoxyphenol to reddish-brown 4-o-methoxyphenol, which can be used to determine its absorbance value by a spectrophotometer at 470 nm, which can be used to find out the activity of the enzyme. The reaction is:
Materials and Instruments
Material:Rice root system, potato tubers, etc. Move The basic procedure for the determination of catalase (CAT) activity can be divided into the following steps: 1. Extraction of enzyme solution: Take 1 g of different rice roots (root surface water absorption), cut it into pieces and put it in a mortar, add 5 mL of 0.1 mol - L-1 Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5), grind it into a homogenate, centrifuge it for 5 min at 4,000 r. min-1, and pour out the supernatant, and then extract the residue with 5 mL of buffer again if necessary, and then merge the supernatant of the two times, and then save the supernatant in a refrigerator (or cold place) for reserve. (Combine the two supernatants and keep them in refrigerator (or cold place) for reserve. 2. Take 2 colorimetric cups of 1 cm optical diameter and add 3 mL of reaction mixture and 1 mL of phosphate buffer (or enzyme solution boiled for 5 min) into one of them as a calibration control, and add 3 mL of reaction mixture and 1 mL of the above mentioned enzyme solution into the other (if the enzyme activity is too high, it can be diluted), immediately turn on the stopwatch to record the time, and then measure the absorbance value with a spectrophotometer at the wavelength of 470 nmT, and read the value at intervals of 1 min (60 s). The absorbance value was measured by spectrophotometer at the wavelength of 470 nmT at 1 min (60 s) intervals for a total of 3 min. 3. 3. Calculation of results: The change in optical density per minute ( A470 is 0.01 unit of activity per minute) indicates the size of the enzyme activity, i.e. Where: A470 - change in absorbance during the reaction time; Vt a total volume of crude enzyme extract, mL; V1-volume of crude enzyme extract for assay, mL; FW-fresh weight of the sample, g. 0. 01-A470 Each decrease of 0.01 is 1 enzyme activity unit, U; t a reaction time, min. Caveat 1. Enzyme extraction and purification needs to be done at low temperature. 2. H2O2has to be added before the reaction starts, not directly.3 . Enzymatic reactions are fast and timing should be accurate and quick. For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.
Reagents:
(1) 0.1 mol - L
-1
Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5): take 12.114 g of Tris (Tris), dilute with water, adjust pH 8.5 with HCl and then volume 1000 mL.
(2) 2 mol - L
-1
phosphate buffer (pH 6.0).
Reserve solution A: 0.2 mol - L
-1
NaH
2
PO
4
solution (27.8 g NaH
2
PO
4
- H
2
O to 1000 mL).
Reservoir B: 0.2 mol - L
-1
Na
2
HPO
4
solution (53. 65 g Na
2
HPO
4
- 7H
2
O or 71.7 g Na
2
HPO
4
- 12H
12H
O to 1000 mL )
o
Separately take 87.7 mL of Reservoir A and 12.3 mL of Reservoir B and mix well and dilute to 200 mL. o
Reaction mixture: take 2 mol・L
-1
phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) 50 mL, hydrogen peroxide 0.028 mL, guaiacol 0.019 mL.
3. Equipment: spectrophotometer, pipette, centrifuge, stopwatch, mortar, balance and so on.