Determination of leaf photosynthetic rate by the modified half-leaf method
Photosynthesis is a process in which green plants absorb light energy to synthesize CO2 and H2O into organic matter and release O2. Photosynthesis rate is an important index to reflect the physiological traits of plants, and it is also the main basis for estimating the photosynthetic production capacity of plants. Photosynthesis rate can be measured from the absorption of CO2, the release of O2 or the increase of dry matter (organic matter). In this experiment, we will learn the principle and process of the modified half-leaf method to determine the photosynthetic rate of leaves.
Principle
The basic principle of the modified half-leaf method for determining the photosynthetic rate of leaves is that plants photosynthesize to form organic matter, and the accumulation of organic matter can lead to an increase in the dry weight per unit area of the leaf blade, but the leaf blade accumulates photosynthesized products under the light and at the same time, it will also transport assimilates out of the leaf blade through the transport tissues, which will make the measured dry weight accumulation value biased low. To eliminate this bias, half of the leaf to be measured must be blacked out, and the reduction in dry weight per unit area on the blacked-out side of the leaf measured over the same period of time as an estimate of assimilate output (and respiratory consumption). This is the basic principle of the classical half-leaf method for determining photosynthetic rate. Two sets of leaves with good symmetry and uniform thickness must be selected for the measurement, one set of leaves is used to measure the initial value of dry weight, and the other (half-leaf darkened) set of leaves is used to measure the final value of dry weight. The half-leaf method is not only cumbersome, but also has a large error.
The "modified half-leaf method" uses methods such as scalding, ring-cutting or chemical reagent treatments to damage the living cells of the petiole phloem to prevent photosynthetic products from being exported from the leaf (these treatments hardly affect the transport of water and inorganic salts from the xylem to the leaf), and only one set of leaves is used, and there is no need to blacken half of the leaves, which not only simplifies the steps but also improves the accuracy of the measurements.
Operation method
Determination of leaf photosynthetic rate by the modified half-leaf method
Principle
The basic principle of the modified half-leaf method for determining the photosynthetic rate of leaves is that plants photosynthesize to form organic matter, and the accumulation of organic matter can lead to an increase in the dry weight per unit area of the leaf blade, but the leaf blade accumulates photosynthesized products under the light and at the same time, it will also transport assimilates out of the leaf blade through the transport tissues, which will make the measured dry weight accumulation value biased low. To eliminate this bias, half of the leaf to be measured must be blacked out, and the reduction in dry weight per unit area on the blacked-out side of the leaf measured over the same period of time as an estimate of assimilate output (and respiratory consumption). This is the basic principle of the classical half-leaf method for determining photosynthetic rate. Two sets of leaves with good symmetry and uniform thickness must be selected for the measurement, one set of leaves is used to measure the initial value of dry weight, and the other (half-leaf darkened) set of leaves is used to measure the final value of dry weight. The half-leaf method is not only cumbersome, but also has a large error. The "modified half-leaf method" uses methods such as scalding, ring-cutting or chemical reagent treatments to damage the living cells of the petiole phloem to prevent photosynthetic products from being exported from the leaf (these treatments hardly affect the transport of water and inorganic salts from the xylem to the leaf), and only one set of leaves is used, and there is no need to blacken half of the leaves, which not only simplifies the steps but also improves the accuracy of the measurements.
Materials and Instruments
Material: living plant leaves. Move The basic procedure for determining leaf photosynthetic rate by the modified half-leaf method can be divided into the following steps: Select 10 representative leaves (e.g., the part of the leaf on the plant, age, light condition, etc. should be the same as far as possible) in the field in advance, and hang them up and number them, and start the experiment at 7-8 o'clock in the morning on a sunny day.
Reagents:
① Paraffin wax
② 5%~10% trichloroacetic acid
Equipment:
① Analytical balance
① Oven
③ Weighing dish (or aluminum box)
④ Scissors
⑤ Blade
⑥ Metal or plexiglass template
⑦ Punch
⑧ Gauze
⑨ Hot water bottle or other portable heating device
⑩ Clip with gauze attached
⑪ Brush
⑫ Enameled plate with lid
Cards
⑭ Pencil
According to the morpho-anatomical characteristics of the material, you can choose any one of the following.
(1) For dicotyledonous plants with better lignification of petioles and easy separation of phloem and xylem, use a razor blade to cut the outer bark of the petiole in a loop 0~5 cm wide and cut off the phloem for transportation.
(2) For monocotyledonous plants such as wheat and rice, in which the phloem and xylem are difficult to be separated, a gauze-wrapped test-tube clip that has just been soaked in boiling water (water temperature of 90℃ or more) can be used to hold the leaf sheath and the stalks therein and scald them for about 20 s in order to injure the phloem. Corn and other leaves in the vein is thicker, boiling water can not be thoroughly scalded, can be used to dip the brush burned to 110 ~ 120 ℃ paraffin scald its leaf base.
(3) on the petiole is thin and vascular bundles scattered, ring peeling method is not easy to grasp or ring cut petiole is easy to break some plants (such as cotton), can be used chemical ring cutting. That is, with a brush dipped in trichloroacetic acid (protein precipitant) spot coating petioles to kill sieve tube living cells.
In order to keep the leaves from drooping after the above treatment, tinfoil, rubber or plastic tubes can be used to wrap around the leaves to keep the original angle of attachment.
3. Cutting samplesAfter the leaf base treatment, you can cut the sample, record the time, and start the photosynthetic rate measurement. Generally, half of the symmetrical leaves were cut off according to the number order (the midvein was not cut off), and according to the number order, the leaves were clamped on the moist gauze, put into an enameled plate with a lid, kept in the dark, and brought back to the room. The other half of the leaf with the midvein was left on the plant for photosynthesis. After 4-5 h (the treatment time can be shortened for samples with good light and large leaves), the other half of the leaves were cut off sequentially. The other half of the leaves were cut sequentially and brought back to the plant in moist gauze, also according to the number. The order and time spent on the two leaf cuttings should be consistent as much as possible, so that each leaf experiences the same number of hours of light.
4. weighing comparisonThe two halves of the same number of the corresponding parts of the leaf stacked together, with the appropriate size of the template and one-sided blade (or punch), in the middle of the half of the leaf cut (punch) under the same size of the leaf area, light and dark treatment of the leaf block were placed in 105 ℃ to kill 10 min, and then baked at 80 ℃ to a constant weight (about 5 h), in the analytical balance were weighed, and the data will be measured in Table 17-1, and calculate the results. Calculate the results.
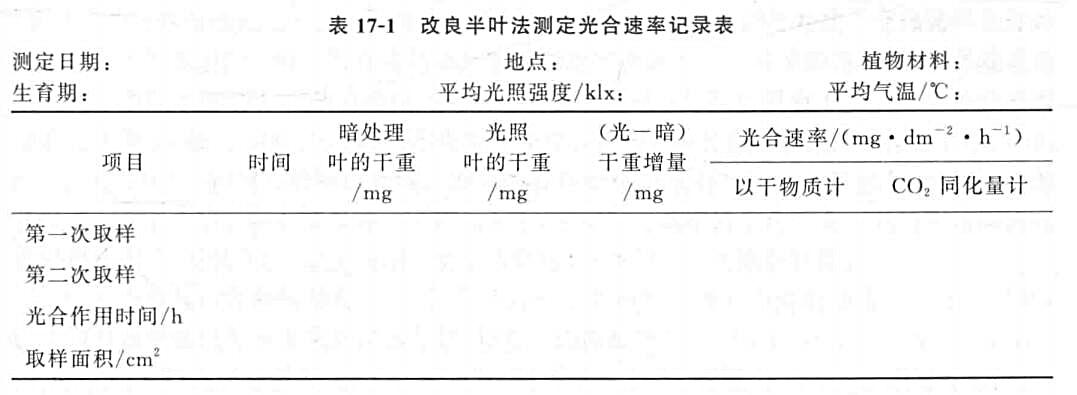
(1) Calculate according to dry matter:

(2) Calculation by CO2 assimilation: Since the photosynthetic products in leaves are mainly carbohydrates such as sucrose and starch, and 1 mol of CO2 can form 1 mol of carbohydrates, multiply the weight of dry matter by a factor of 1.47 (44/30 = 1.47), and the amount of CO2 assimilated by unit leaf area per unit of time will be obtained ( mg・dm-2・h-1 ).
The above is the determination and calculation of the total photosynthetic rate, if you need to determine the net photosynthetic rate, just the first half of the leaf retrieval, immediately cut pieces, drying can be, and other steps and calculation methods are the same as above.
Caveat
1. If the scald is not complete, part of the organic matter can still be transported out of the country and the measurement results are low. Where there is a clear water-impregnated appearance, this indicates that the scald is complete. Scald completely is one of the keys to the success of the method.
2. for wheat, rice and other gramineous plants, scalded parts to choose in the upper part of the leaf sheath close to the leaf occipital 5 mm is good, can avoid photosynthetic products to the leaf sheath in the transportation, but also can avoid the leaf occipital at the scalded and make the leaf drooping.
For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.
