Determination of plant respiration rate
Respiration rate is one of the most important indicators of the strength of plant life activities. The size of the respiration rate of plants varies depending on the type of plant, type of tissue, fertility period, and is also affected by the external environment. Organizations with high respiration rates generally have strong metabolism, while low respiration rates indicate weak metabolic activities. Therefore, the determination of respiration rate is necessary in the study of plant physiology and the practice of agricultural production.
There are many methods for its determination, such as infrared CO2 analysis, oxygen electrode method, Watt's respirometer method, respiratory bottle method and so on. In this experiment, we used the wide-mouth bottle method to determine the respiration rate of plants and compare the respiration rate of plants at different germination stages.
Principle
Add a certain amount of Ba(OH )2 solution in a wide-mouth bottle, the CO2 released by the respiration of plant material can be absorbed by the Ba(OH )2 in the bottle, and then titrate the remaining alkali with oxalic acid solution (the reaction is as follows), from the difference between the blank and the sample of the two consumption of oxalic acid solution, we can calculate the amount of CO2 released, and express the respiration rate in terms of the amount of CO2 released.
Ba(OH) 2 + CO2 → BaCO3 ↓ + H2O (20-1)
Ba(OH) 2 (remaining) + H2C2O4 ↓ +2H2O (20-2)
Operation method
Determination of plant respiration rate
Principle
Add a certain amount of Ba(OH)2 solution in a wide-mouth bottle, the CO2 released by the respiration of plant material can be absorbed by the Ba(OH)2 in the bottle, and then titrate the remaining alkali with oxalic acid solution (the reaction is as follows), from the difference between the blank and the sample of the two consumption of oxalic acid solution, you can calculate the amount of CO2 released, and express the respiration rate in terms of the amount of CO2 released.Ba(OH)2 + CO2 → BaCO3 ↓ +H2O (20-1) Ba(OH)2(remaining) + H2C2O4↓ + 2H2O (20-2) +H2O (20-1) Ba(OH)2(remaining) + H2C2O4↓ +2H2O (20-2)
Materials and Instruments
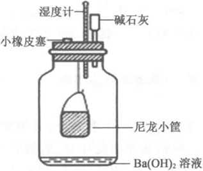
Materials: Wheat at different stages of germination. Move The basic procedure for determining the rate of plant respiration can be divided into the following steps. 1: 1. Assemble the wide-mouth flask respiration device: Take a 500 mL wide-mouth flask and add a three-hole rubber stopper. One hole is inserted into a drying tube containing soda lime. Make its absorption of CO2 in the air , to ensure that in the determination of respiration into the breathing bottle of air without CO2; a hole into the thermometer; another hole of about 1 cm in diameter, for titration. The other hole is about 1 cm in diameter for titration. Normally, the bottle is plugged tightly with a small rubber stopper. A small hook is installed under the stopper to hang a small basket made of nylon window screen for plant material. The whole device is shown in Figure 20-1. 2. Blank titration: pull out the small rubber stopper on the titration hole, use the alkali buret to accurately add 0.05 mol - L 1 Ba (OH ) 2 solution 20 mL into the bottle, and then plug the titration hole tightly. Shake the bottle fully for 3~5 min, after all the CO2 in the bottle is absorbed, pull out the rubber stopper and add 3 drops of phenol, insert the acid buret into the hole, and titrate the blank with 1/44 mol - oxalic acid solution until the red color disappears, and then write down the amount of oxalic acid solution (mL), that is, the blank titration value. 3. Sample titration: pour out the waste liquid, first tap water, and then new boiling (to drive away the CO2 in the water) and cooled distilled water to wash a wide-mouth bottle, add 20 mL of Ba (OH ) 2 solution in the bottle, take the wheat seeds to be tested 100, while weighing out the weight of the wheat seeds, loaded into a small basket, open the rubber stopper, and then quickly hanged in the rubber stopper on the hook, plugged the stopper, and began to record the time. After 30 min, during which gently shaking several times, so that the solution surface of BaCO, film broken, in favor of the full absorption of CO2. After the predetermined time, gently open the stopper, quickly take out the small basket, and immediately re-corked. Shake fully for 2 min, so that the bottle of CO2 is completely absorbed, pull out the small rubber stopper, add 3 drops of phenol, titrate with oxalic acid solution as before. Note down the amount of oxalic acid solution, that is, the sample titration value. 4. Determine the amount of oxalic acid solution consumed by 100 sprouted wheat seeds according to step 3. 5 . Calculate the respiration rate: The unit of respiration rate can be generally used mgCO2 - g-1FW - h-1, where the titration value is in mL, mgCO2-mL-1 oxalic acid = 1. Caveat 1. When adding samples, try to prevent the air in the room and the gas exhaled from the mouth from entering into the bottle. 2. Pay attention to the end point of the titration. For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.
Equipment: 1 set of wide-mouth bottle respirometry device, electronic balance, 1 each acid and alkaline buret, 1 set of burette rack.
Reagents:
1/44 mol - L
-1
Oxalic acid solution: accurately weigh the recrystallized H
2
C
2
O
4
- 2H
2H
O 2.8651 g was dissolved in evaporated water and condensed to 1000 mL, each milliliter is equivalent to 1 mg CO
2
;
0.05 mol - Ba(OH)
2
solution: Ba(OH)
2
8. 6 g or Ba(OH)
2
- 8H
2
O 15.78 g dissolved in 1000 mL of distilled water, if turbid, wait until the solution is clarified;
Phenol indicator: Dissolve 1 g of phenol in 100 mL of 95% ethanol and store in a dropping bottle.