Determination of total free amino acids in plant tissues
Amino acids are the basic units of proteins and are also the breakdown products of proteins. Nitrogen absorbed and assimilated by plant roots is mainly transported in the form of amino acids and amides. Therefore, the determination of free amino acid content in different parts of plant tissues at different times is of some significance to the study of root physiology and nitrogen metabolism. The purpose of this experiment is to master the principle and method of amino acid determination by the colorimetric method.
Principle
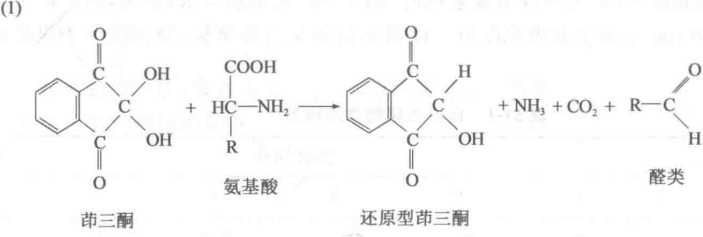
The basic principle for measuring the total amount of free amino acids in plant tissues is the reaction between the free amino group of an amino acid and a hydratrizone (see below). First, the amino acid is deaminated and oxidized, and the hydrated ketone is reduced to the reduced ketone. Next, the reduced ketone is condensed with another oxidized ketone molecule and ammonia to form a blue-purple compound called Ruhemans purple. Its absorption peak is 570 nm, and within a certain range, its color is proportional to the content of amino acids. Accordingly, the absorbance of the reaction product can be measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 570 nm, and the total amount of amino acids in the unknown sample can be calculated from the standard curve. The reaction between proline and stanchotrione produces a yellow color, which needs to be measured separately.

Operation method
Determination of total free amino acids in plant tissues
Principle
The basic principle for measuring the total amount of free amino acids in plant tissues is the reaction between the free amino group of an amino acid and a hydratrizone (see below). First, the amino acid is deaminated and oxidized, and the hydrated ketone is reduced to the reduced ketone. Next, the reduced ketone is condensed with another oxidized ketone molecule and ammonia to form a blue-purple compound called Ruhemans purple. Its absorption peak is 570 nm, and within a certain range, its color is proportional to the content of amino acids. Accordingly, the absorbance of the reaction product can be measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 570 nm, and the total amount of amino acids in the unknown sample can be calculated from the standard curve. The reaction between proline and stanchotrione produces a yellow color, which needs to be measured separately.
Materials and Instruments
Materials: Various plant tissues. Move The basic procedure for the determination of total free amino acids in plant tissues can be divided into the following steps:1. Preparation of standard curve: Take six 20 mL corked graduated test tubes, number them and add reagents according to Table 51-1. Mix well, cover with a glass stopper and heat in a boiling water bath for 15 min, then take them out and put them in a cold water bath for rapid cooling and frequent shaking, so that the red color formed during heating is gradually oxidized by the air and faded until the solution is blue-purple, add 5 mL of non-ammonia evaporated water, mix well and measure the absorbance value at the wavelength of 570 nm in a colorimeter with an optical diameter of 1 cm. Use the amount of amino nitrogen as the horizontal coordinate and the absorbance value as the vertical coordinate to draw the standard curve.Table 51-1 Spiking table for standard curve Caveat 1. Qualified station three ketones should be slightly yellow crystals, if not properly stored, the color will deepen or become reddish, must be recrystallized before use. The method is as follows: 5 g of station three ketone dissolved in 15 mL of hot distilled water, add 0.25 g of activated carbon, gently shaking, when the solution is too thick, can be appropriate amount of water, 30 minutes after the filtration of filter paper, filtrate in the refrigerator overnight that is to say that the analysis of yellowish crystals can be seen, filtered with dry filter paper, and then wash the crystals in 1 mL of steaming water, placed in the desiccator drying and then stored in brown bottles. 2, the reaction between amino acid and station tritone is very sensitive, need to use non-ammonia distilled water. 3, the resulting color is very sensitive at 1 mL. 3. The color generated remains stable within 1 h. After dilution, it should be compared with the color in a short time; when the reaction product is diluted with water, it should be measured within 0.5 h. 4. As oxygen in the air interferes with the color reaction, using ascorbic acid as the reducing agent can improve the sensitivity of the reaction and make the color stable, but because ascorbic acid can also react with lycopene to make the solution too dark, so the amount of ascorbic acid added should be strictly controlled. 5. The temperature of the reaction affects the stability of the color development, heating in a boiling water bath at a temperature of more than 80°C, the solution will easily fade. If the temperature of the reaction exceeds 80°C, the color of the solution will fade easily. If the temperature of the reaction exceeds 80°C, the color of the solution will fade easily. For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.
Equipment: spectrophotometer, thermostatic water bath, balance, volumetric flasks, funnels, triangular flasks, mortar and pestle, stoppered test tubes, pipettes and so on.
Reagents:
(1) Hydration station tritone reagent: weigh 0.6 g of recrystallized rutabione in a beaker, add 15 mL of n-propanol, stir to dissolve. Then add 30 mL of n-butanol and 60 mL of ethylene glycol, and finally add 9 mL of pH 5.4 acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer, mix well, store in a brown bottle, and keep in the refrigerator for spare, effective within 10 days.
(2) pH 5.4 acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer: weigh 54.4 g of crystalline sodium acetate, add 100 mL of non-ammonia distilled water, and heat to boiling on an electric stove to evaporate the volume to half of the original volume. After cooling, add 30 mL of glacial acetic acid, and then add ammonia-free evaporated water to 100 mL.
(3) Standard amino acid solution: weigh 46.8 mg of leucine dried at 80C, dissolve it in a small amount of 10% isopropanol, and then make a volume of 100 mL with 10% isopropanol. 5 mL of this solution should be diluted with non-ammonia evaporated water to 50 mL, that is, the solution will be called as Nitrogen 5 Showa-mL-1 , and the solution will be called as Nitrogen 5 Showa-mL-1 .
1
This is the standard amino acid solution containing nitrogen 5 昭-mL 1.
(4) 0.1% Ascorbic acid: Weigh 50 mg of ascorbic acid and dissolve it in non-ammonia distilled water, then dilute it to 50 mL.
(5) 10% acetic acid: Prepare with ammonia-free evaporated stuffing water, according to V/V.
2. Sample extraction: Take fresh plant samples, wash, dry, cut and mix, quickly weigh 0.5~1.0 g, add 5 mL of 10% acetic acid in a mortar, grind into a homogenate, then use non-ammoniated evaporated stuffing water to 100 mL, shake well, and then filter the supernatant into a triangular flask with dry filter paper for spare.3 . Determination of sample: Put 1 mL of the supernatant into a 20 mL stoppered graduated test tube, add 1 mL of non-ammonia evaporated water, other steps are the same as those for the standard curve, determine the absorbance value of the sample solution, and then find out the nitrogen content of the sample solution on the standard curve according to the absorbance value.4. Calculation of results.C X VFree amino acid content (mg・100 g-] FW) = w x ] 00()X100Where: C I is the nitrogen content of plants g from the standard curve;V - total volume of sample liquid "mL;W■ - sample weight "go Item Tube No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Standard Leucine/mL 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 Ammonia-free distilled water/mL 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 Hydration station triton/mL 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 Ascorbic acid/mL 0. 1 0. 1 0. 1 0. 1 0. 1 0. 1 Amount of amino nitrogen "g 0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 Absorbance value
