Molybdenum hexacarbonyl
Product Manager
Sandra Forbes

Literature

![]() Through a process involving molybdenum hexacarbonyl, the desulfurization of thiols and disulfides can be achieved, effectively eliminating sulfhydryl groups from aryl, benzyl, primary, and secondary alkyl thiols, as well as breaking the S-S bonds in disulfides. This method is compatible with a wide range of functional groups and remains unaffected by steric hindrance.
Through a process involving molybdenum hexacarbonyl, the desulfurization of thiols and disulfides can be achieved, effectively eliminating sulfhydryl groups from aryl, benzyl, primary, and secondary alkyl thiols, as well as breaking the S-S bonds in disulfides. This method is compatible with a wide range of functional groups and remains unaffected by steric hindrance.
Z. Wang, Y. Kuninobu, M. Kanai, Synlett, 2014, 25, 1869-1872.
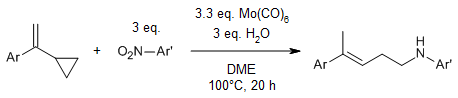
Additionally, a molybdenum-catalyzed reductive hydroamination of vinylcyclopropanes with nitroarenes yields substituted homoallylamines in high efficiency. This reaction avoids the use of noble metal catalysts, as Mo(CO)6 serves dual roles as both the catalyst and the reducing agent. This approach offers a practical route for the selective production of substituted homoallylamines from readily accessible nitroarenes.
J.-L. Lu, Z. Zhang, J.-T. Deng, A.-J. Ma, J.-B. Peng, Org. Lett., 2023, 25, 2991-2995.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00781
Quoted from: https://www.organic-chemistry.org/chemicals/reductions/molybdenum-hexacarbonyl.shtm
Aladdinsci: https://www.aladdinsci.com
